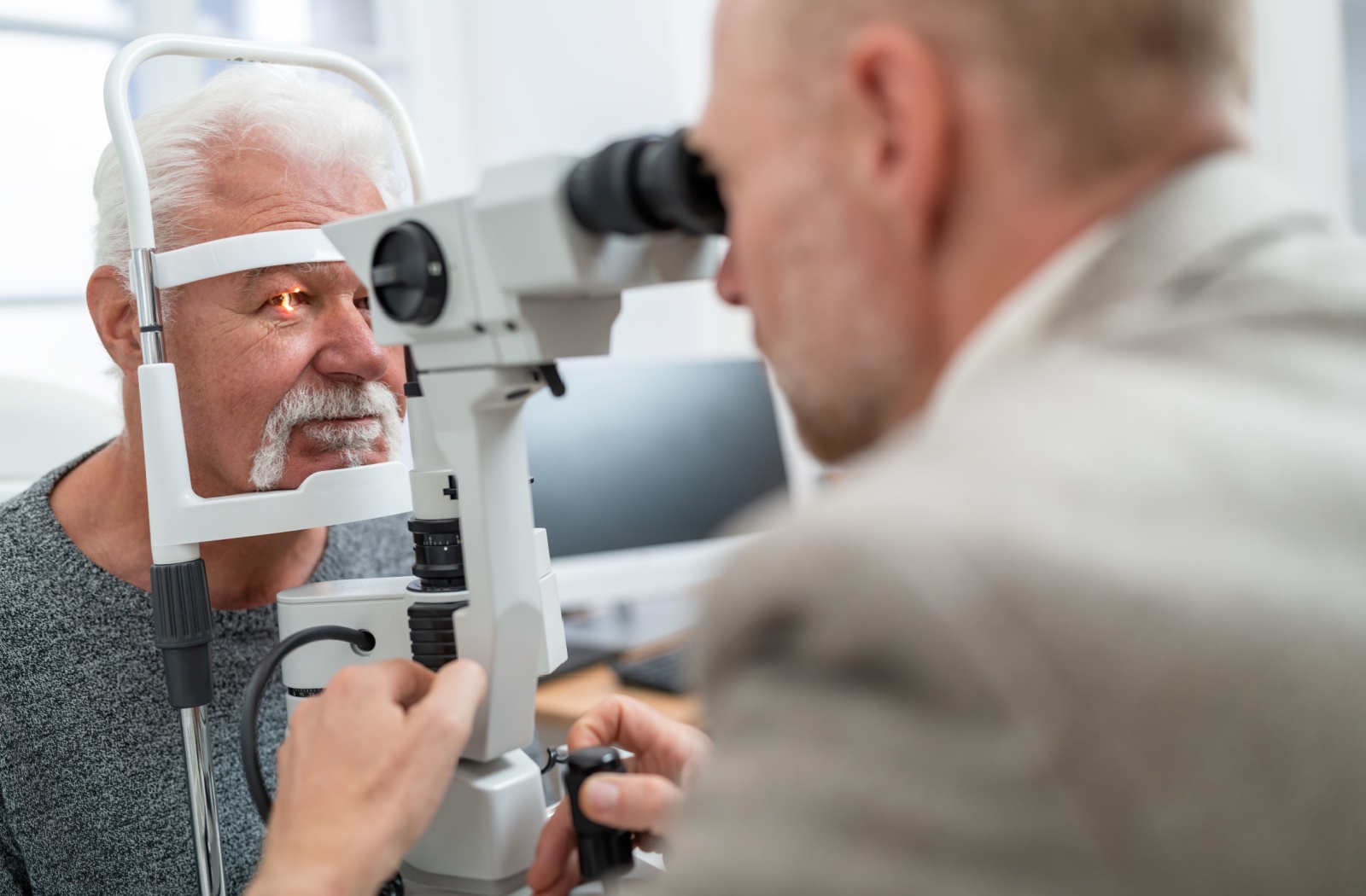
Your eyes do more than help you see—they can also reveal important clues about your overall health. A comprehensive eye exam doesn’t just assess your vision; it can detect signs of systemic conditions like diabetes by identifying changes in the blood vessels and other structures within the eye.
Diabetes-related damage often shows up in the eyes before any symptoms are noticeable elsewhere in the body. That’s why regular eye exams are essential—not just for maintaining clear vision, but also for spotting potential health issues early, when intervention can be more effective and complications can be better managed.
Can Regular Eye Exams Detect Signs of Diabetes?
During a comprehensive eye exam, your eye doctor can detect changes in the blood vessels of your retina, fluid leakage under the macula, or other abnormalities that may indicate diabetes.
By spotting these signs early, your eye doctor can recommend further testing or connect you with your primary care provider. Detecting issues sooner gives you the chance to manage your health proactively and lowers the risk of complications that could impact both your vision and overall well-being.
What Your Eyes Say About Your Health
Your eyes, sometimes called “windows to the soul,” also offer a clear view into your overall health. The blood vessels and structures inside them can reveal signs of health issues occurring elsewhere in the body.
Many diseases, including diabetes, can manifest in the eyes before other symptoms become noticeable—often allowing your eye doctor to detect issues before a general healthcare provider. This makes regular eye exams an essential part of maintaining not only good vision but good overall health.
What Diseases Can be Detected in an Eye Exam?
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes sugar (glucose) with the help of insulin—a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar. When there isn’t enough insulin or the body can’t properly use the insulin produced, it can lead to elevated blood sugar levels.
Over time, high blood sugar can cause complications, including problems with the eyes. One of the most common issues is diabetic retinopathy, in which high blood sugar damages the blood vessels in the retina—the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Diabetes can also lead to other complications, such as:
- Macular edema: A condition where fluid builds up in the macula—the central part of your retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision. It can cause blurry or distorted vision and may progress to permanent damage if left untreated.
- Glaucoma: Elevated blood sugar can damage the optic nerve, leading to glaucoma. This condition causes pressure buildup inside the eye, which can harm the optic nerve and potentially cause blindness.
- Cataracts: Diabetes significantly increases the risk of developing cataracts—the clouding of the eye’s lens—which can impair vision and often requires surgery to replace the lens.
Signs and symptoms of diabetic eye disease may include:
- Blurry or fluctuating vision
- Frequent prescription changes
- Blind spots
- Flashes of light
- Floaters
- Sudden vision loss

What Is a Diabetic Eye Exam?
For individuals already diagnosed with diabetes, a specialized exam—called a diabetic eye exam—is essential each year. This exam differs slightly from a standard eye exam by focusing specifically on diabetic eye diseases and how to prevent their progression.
During a diabetic eye exam, your eye doctor may perform the following:
- Dilation: Eye drops are used to widen your pupils, allowing a better view of the back of the eye, including the retina and macula.
- Retinal photography or imaging: Advanced cameras capture detailed images of the retina to monitor changes over time.
- OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography): This test provides cross-sectional images of the retina, revealing swelling or fluid buildup.
Because diabetic eye diseases can progress silently, annual exams are crucial—even if you don’t notice any vision changes. These exams can uncover early signs and enable timely treatment.
Preventing Diabetic Eye Complications
Whether you’re living with diabetes or looking to prevent it, making proactive lifestyle choices can lower your risk of complications and support long-term eye health.
- Get regular eye exams: Annual eye exams are essential if you have diabetes.
- Manage your blood sugar: Follow a balanced diet and take any prescribed medications to keep blood sugar levels under control.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Exercise, movement, and weight management can help lower your diabetes risk.
- Quit smoking: Smoking increases your risk of diabetic eye diseases—quitting is a vital step for prevention.
- Stay informed: Understanding the link between diabetes and eye health helps you make better choices and prioritize vision care.
Protect Your Vision, Protect Your Health
Protecting your vision starts with understanding how your overall health, especially conditions like diabetes, can affect your eyes. Regular, comprehensive eye exams are a key part of early detection and ongoing care. Even if you aren’t experiencing symptoms, subtle changes in your eyes can reveal more than you think. At The Eye Avenue, we take a whole-person approach to eye care, helping you stay ahead of potential problems before they progress. Book your next eye exam today and take an important step toward protecting your sight and your health.